Gi Manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS) can manifest as gastrointestinal (GI) issues and symptoms include constipation, bloating, and abdominal pain. These manifestations are common in EDS due to the connective tissue abnormalities affecting the digestive system.
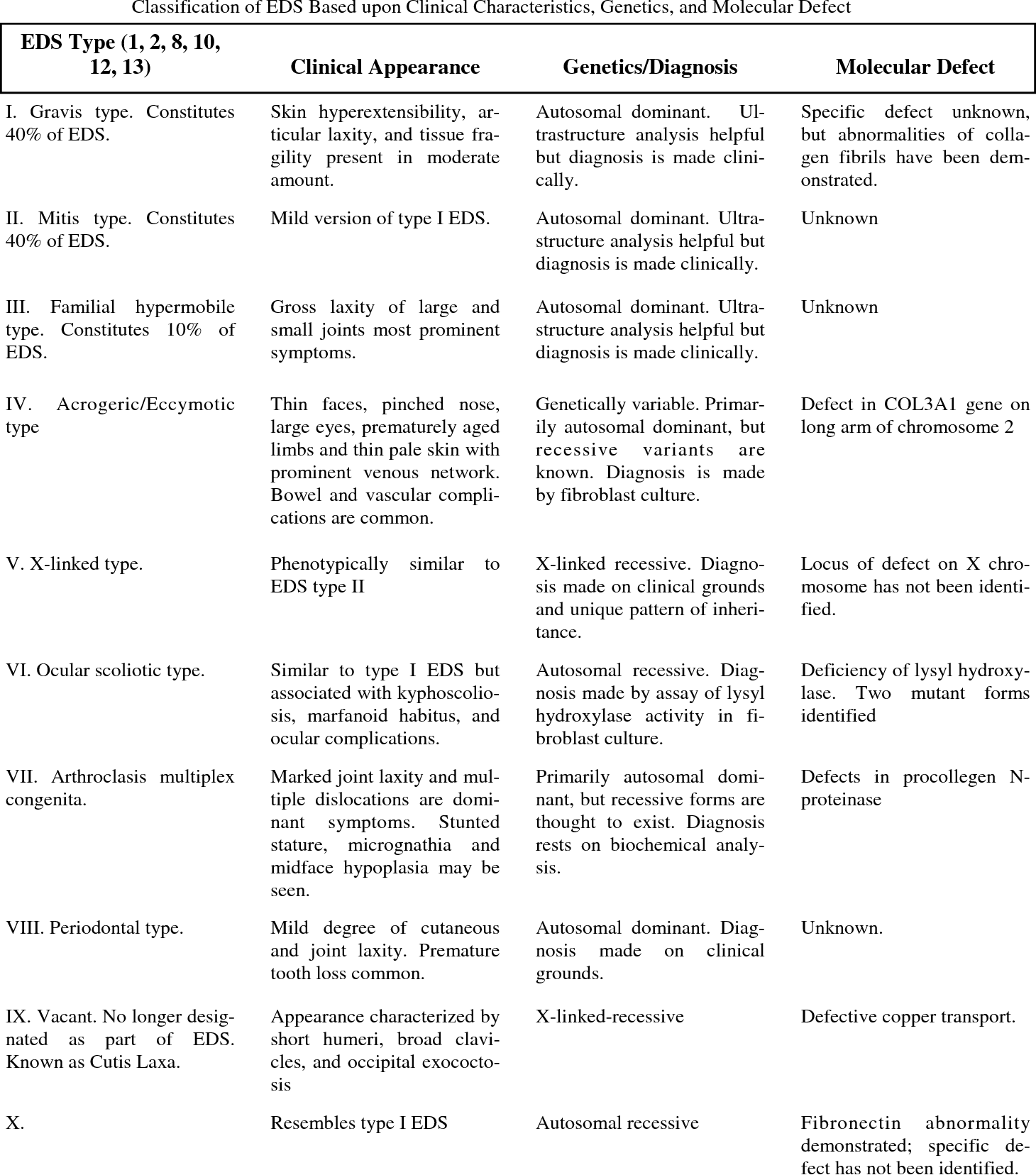
EDS is a group of connective tissue disorders characterized by hypermobility, skin fragility, and joint hypermobility. Individuals with EDS may experience a range of GI symptoms that can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding the GI manifestations of EDS is crucial for healthcare providers to effectively diagnose and manage the condition.
We will explore the specific GI manifestations of EDS, their impact on patients, and potential strategies for managing these symptoms. By gaining insight into these manifestations, individuals with EDS and their healthcare providers can work together to improve their overall well-being.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Types Of Gastrointestinal Involvement
Individuals with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome may experience various gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations due to the connective tissue abnormalities affecting the digestive system. Understanding the types of gastrointestinal involvement can help in managing symptoms effectively.
Common Gi Symptoms
- Abdominal pain: A frequent complaint among EDS patients.
- Gastroesophageal reflux: Heartburn and regurgitation are common.
- Constipation: Difficulty in passing stools due to motility issues.
Rare Gi Symptoms
- Intussusception: Telescoping of the intestines, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Gastroparesis: Delayed gastric emptying leading to bloating and nausea.
- Mallory-Weiss tear: Esophageal tear from severe vomiting episodes.

Credit: www.ehlers-danlos.com
Diagnosis And Evaluation
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a group of connective tissue disorders that can affect various parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal (GI) system. Diagnosis and evaluation of GI manifestations in EDS are crucial for effective management and treatment. Understanding the clinical assessment and diagnostic tests for GI manifestations is essential in providing comprehensive care for individuals with EDS.
Clinical Assessment
When evaluating GI manifestations in individuals with EDS, clinical assessment plays a key role in identifying symptoms and their impact on daily life. Healthcare professionals assess symptoms such as chronic abdominal pain, gastrointestinal dysmotility, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Additionally, they consider the presence of other EDS-related symptoms that may contribute to GI issues, such as joint hypermobility and skin hyperextensibility.
Diagnostic Tests For Gi Manifestations
Diagnostic tests are utilized to confirm and further investigate GI manifestations in individuals with EDS. These tests may include:
- Endoscopy to visualize the upper GI tract and identify any structural abnormalities or inflammation.
- Colorectal transit studies to assess motility and transit time of the digestive system.
- Manometry to evaluate esophageal and anorectal function, providing insights into motility disorders.
These diagnostic tests aid in identifying specific GI issues and guiding treatment strategies tailored to the individual’s needs.
Treatment Approaches
Individuals with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome often experience gastrointestinal manifestations that can be challenging to manage. Treatment approaches for these symptoms may include dietary modifications, medication to alleviate pain and improve motility, physical therapy to strengthen the abdominal muscles, and psychological support to manage the impact on quality of life.
Medication Management
Medication management is one of the primary approaches used to treat Gi manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. The aim of medication is to alleviate the symptoms and improve the quality of life of the patient. The drugs used for treating the condition are usually prescribed based on the specific symptoms and severity of the condition. Some of the commonly used medications include:- Antidiarrheal Medications: These are used to alleviate diarrhea and abdominal pain. Loperamide is the most commonly used antidiarrheal medication that slows down the movement of the intestines, thereby reducing diarrhea.
- Pain Relievers: Pain relievers such as Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to alleviate pain and inflammation. However, long-term use of NSAIDs can cause adverse effects on the digestive system and should only be used under medical supervision.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial to the digestive system. They help to restore the balance of bacteria in the gut, thereby reducing symptoms such as diarrhea and bloating.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications can play a significant role in managing the Gi manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Patients are advised to avoid foods that trigger their symptoms and to eat small, frequent meals throughout the day. Some of the dietary modifications that can help manage the condition include:- Fiber: Eating a high-fiber diet can help regulate bowel movements and reduce constipation. However, some patients may find that high-fiber diets exacerbate their symptoms and should only be consumed under medical supervision.
- Low-FODMAP Diet: A low-FODMAP diet is a diet low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols. This diet has been found to be effective in reducing symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for patients with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of dehydration.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to manage the Gi manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Surgery is usually recommended when other treatment approaches have failed to alleviate the symptoms and improve the quality of life of the patient. Some of the surgical interventions that can help manage the condition include:- Colectomy: Colectomy is the surgical removal of the colon. This surgery is usually recommended for patients with severe symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, bleeding, and pain.
- Gastrointestinal Resection: Gastrointestinal resection is the surgical removal of a part of the digestive system. This surgery is usually recommended for patients with severe symptoms such as intestinal obstruction and bleeding.
- Colostomy: Colostomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating an opening in the abdomen and attaching the colon to the opening. This surgery is usually recommended for patients with severe symptoms such as fecal incontinence and chronic constipation.
Management Of Complications
Managing the complications associated with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is crucial for improving the quality of life for individuals with this condition. The gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations of EDS can present challenges, requiring careful management to prevent and address potential complications.
Dealing With Bowel Perforations
Bowel perforations are a serious complication that individuals with EDS may face. Immediate medical attention is essential in the event of a suspected bowel perforation. Surgical intervention may be required to repair the perforation and prevent further complications.
Addressing Malnutrition
Malnutrition can be a concern for individuals with EDS, particularly due to gastrointestinal dysfunction. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a nutritional plan that addresses any malabsorption issues and ensures adequate nutrient intake.
Lifestyle Considerations
When living with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS), it’s crucial to consider various lifestyle factors to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Lifestyle considerations play a significant role in alleviating the impact of the condition. From exercise and physical therapy to psychological support, these aspects can make a difference in managing the manifestations of EDS.
Exercise And Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and physical therapy are essential for individuals with EDS to maintain muscle strength and joint stability. Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, and gentle yoga can help in improving flexibility and reducing the risk of injury. Customized physical therapy programs can also aid in strengthening connective tissues and improving overall mobility.
Psychological Support
Psychological support is crucial for individuals with EDS, as the condition can impact mental well-being. Counseling and support groups can provide a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies. It’s important to address the emotional challenges that come with EDS and seek professional help if needed to manage anxiety, depression, and other psychological aspects.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Research And Future Directions
Research has made significant strides in understanding the gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS). However, there is still much to be learned about the mechanisms behind these symptoms and effective treatment options. This article will explore the current studies on GI manifestations and potential therapeutic advances for EDS patients.
Current Studies On Gi Manifestations
Studies have shown that GI symptoms are prevalent among patients with EDS, with up to 88% experiencing some form of GI issue. These symptoms can include constipation, diarrhea, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and abdominal pain. The exact cause of these symptoms is not yet fully understood, but researchers believe they may be due to abnormalities in the connective tissue that lines the GI tract.
Recent studies have focused on identifying the specific genetic mutations that cause EDS and how they relate to GI symptoms. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Medical Genetics found that patients with EDS have a higher incidence of mutations in genes related to gut motility and absorption. Another study published in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition found that EDS patients with GI symptoms had significantly lower levels of collagen in their GI tract.
Potential Therapeutic Advances
While there is currently no cure for EDS, there are several potential therapeutic advances being explored for the treatment of GI symptoms. One promising area of research is the use of probiotics to improve gut health. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology found that patients with EDS who took a probiotic supplement experienced a significant reduction in abdominal pain and bloating.
Another potential treatment option is the use of anti-inflammatory medications. A study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology found that EDS patients with GI symptoms had significantly higher levels of inflammation in their gut, which could be reduced with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Finally, researchers are exploring the use of collagen supplements to improve the connective tissue in the GI tract. While this is still a relatively new area of research, some studies have shown promising results. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that collagen supplementation improved gut integrity and reduced inflammation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Conclusion
To sum up, understanding the gastrointestinal manifestations of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome is crucial for proper management. Recognizing symptoms early can lead to better treatment outcomes. Stay informed, seek medical guidance, and empower yourself with knowledge to navigate this complex condition effectively.
Your health journey matters.